Deploy Containers to Google Cloud Run from GitLab
Essay - Published: 2022.07.12 | 4 min read (1,046 words)
containers | docker | gitlab | google-cloud
DISCLOSURE: If you buy through affiliate links, I may earn a small commission. (disclosures)
Manual deployments are slow and prone to breakage. In 2022 your deployment pipeline should be entirely automated - and there are a lot of tools available to make this easier than ever.
In this post, I'll walk you through how to build and deploy your containerized app from your GitLab repo to Google Cloud Run.
Table of Contents
GitLab to Google Cloud Run
First, let's go over how the approach works from a high level.
The components we'll be using are:
- GitLab - Where our code is stored
- Application code
- Dockerfile -
Dockerfile - GitLab CI Config -
gitlab-ci.yml - Cloud Build config -
cloudbuild.yaml
- Google Cloud Build - Used to build a container with our application code and dockerfile
- Google Cloud Run - Will host our container(s)
Read how / why I use Cloud Run to keep costs low.
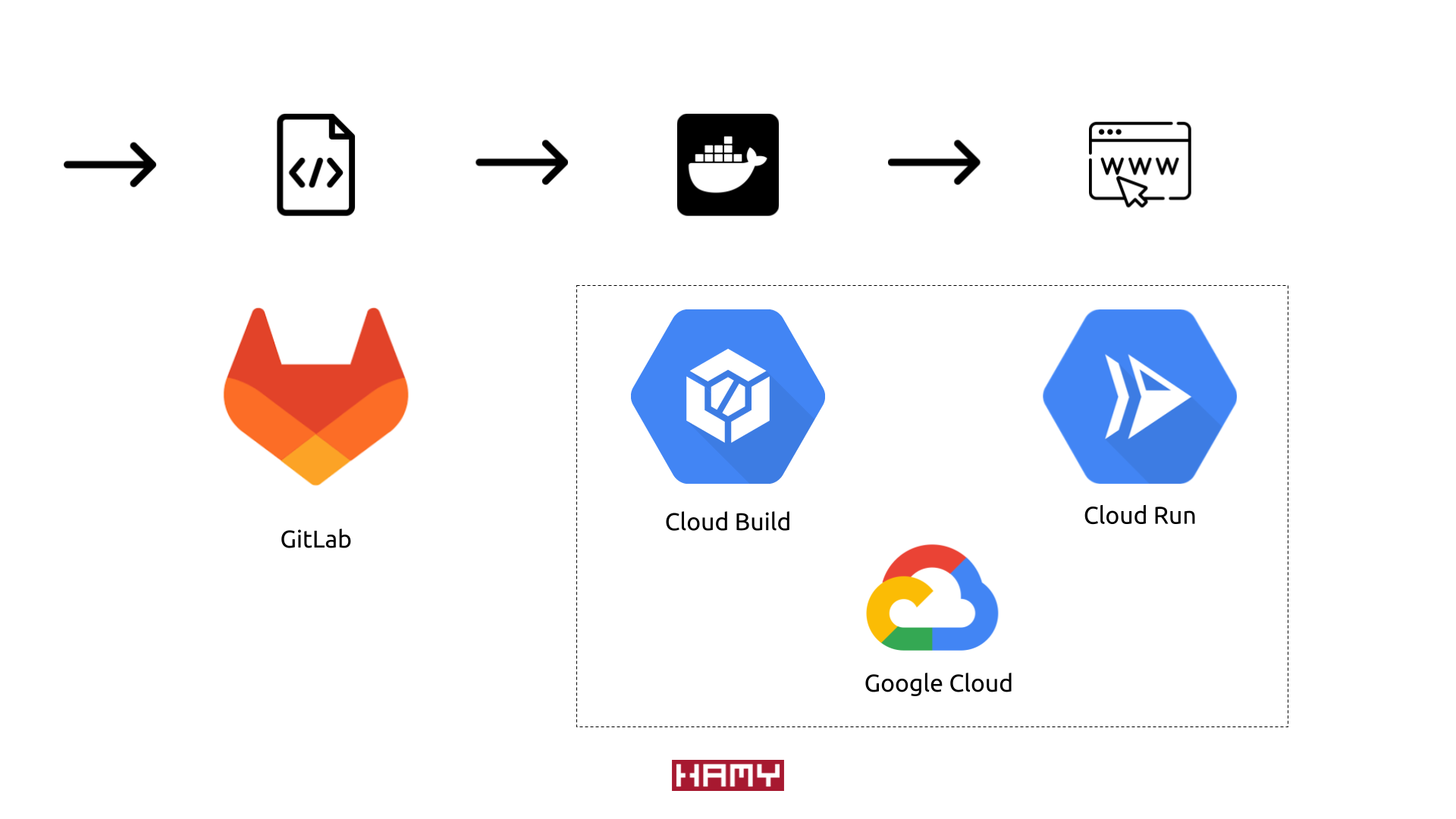 GitLab to Cloud Run deployment pipeline
GitLab to Cloud Run deployment pipeline
When we push an update to our GitLab repo's main branch we'll trigger our build and deploy pipeline:
- GitLab will run our CI logic using the
gitlab-ci.ymlfile- This will instantiate the Google Cloud SDK
- Then it will use the SDK to package our code and trigger Cloud Build
- Cloud Build will start a build based on the
cloudbuild.yaml- Build a container image using the
Dockerfile - Push the image to our Google Cloud project
- Deploy the image to Cloud Run
- Build a container image using the
For this example, I'll be using the CloudSeed SaaS template which includes two pre-containerized apps to deploy:
- Web - Dockerized Sveltekit
- App - Dockerized .NET
Let's get started.
Setup Google Cloud Project
The first thing we need to do is setup our Google Cloud project so that it can work with Cloud Build and Cloud Run.

- Create a Google Cloud Project
- Enable Cloud Build
Cloud Build > Settings- Click
View API - Click
Enable - Wait a few seconds for permissions to load
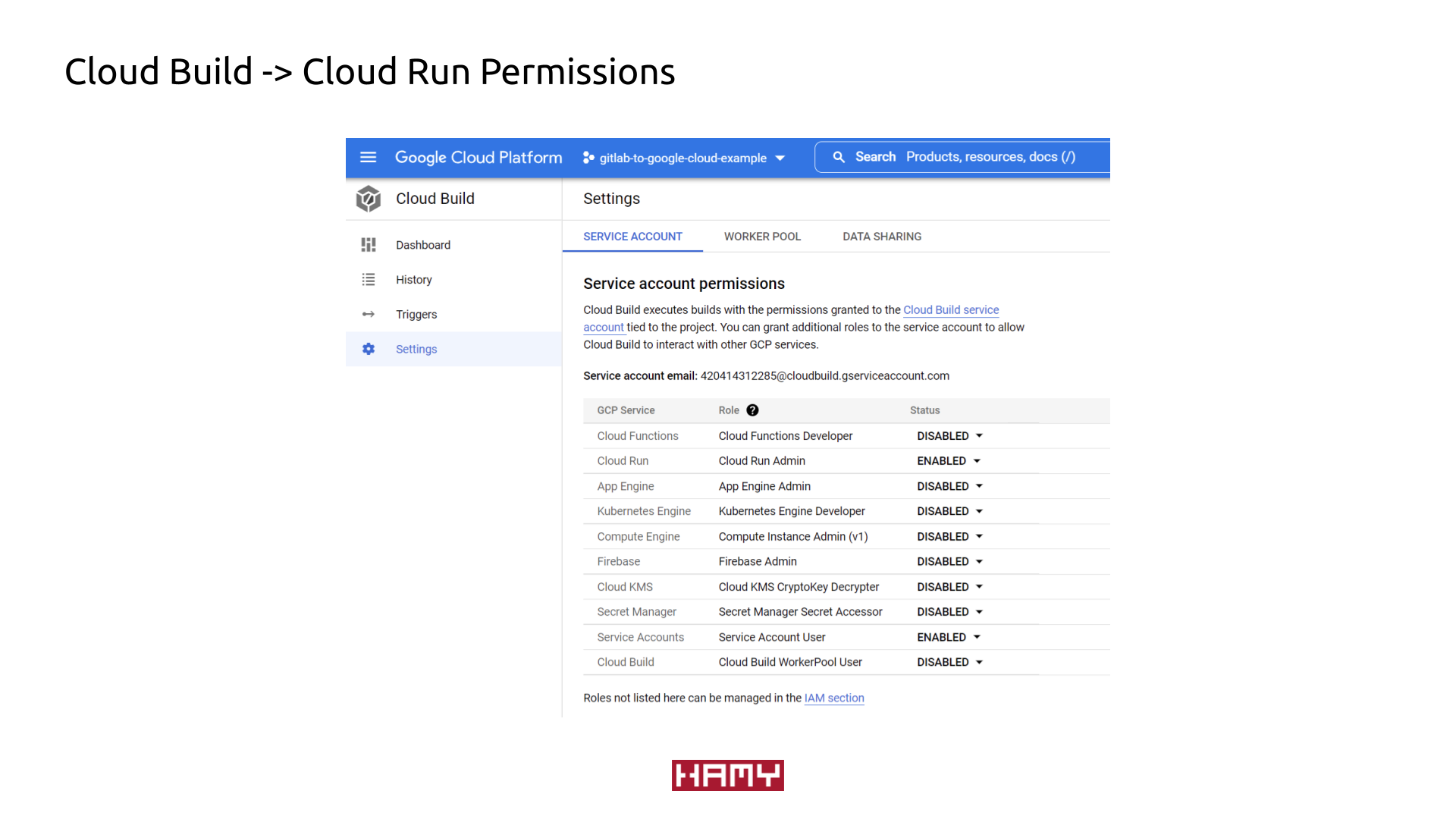
- Set Cloud Build permissions
Cloud Build > SettingsCloud Run Admin: EnabledService Accounts: Enabled
- Create a Cloud Build service account
IAM & Admin > Service Accounts- Click
Create Service Account - Name:
GitLab CI Cloud Build - Role:
Cloud Build Service Agent,Cloud Build Editor
- Click
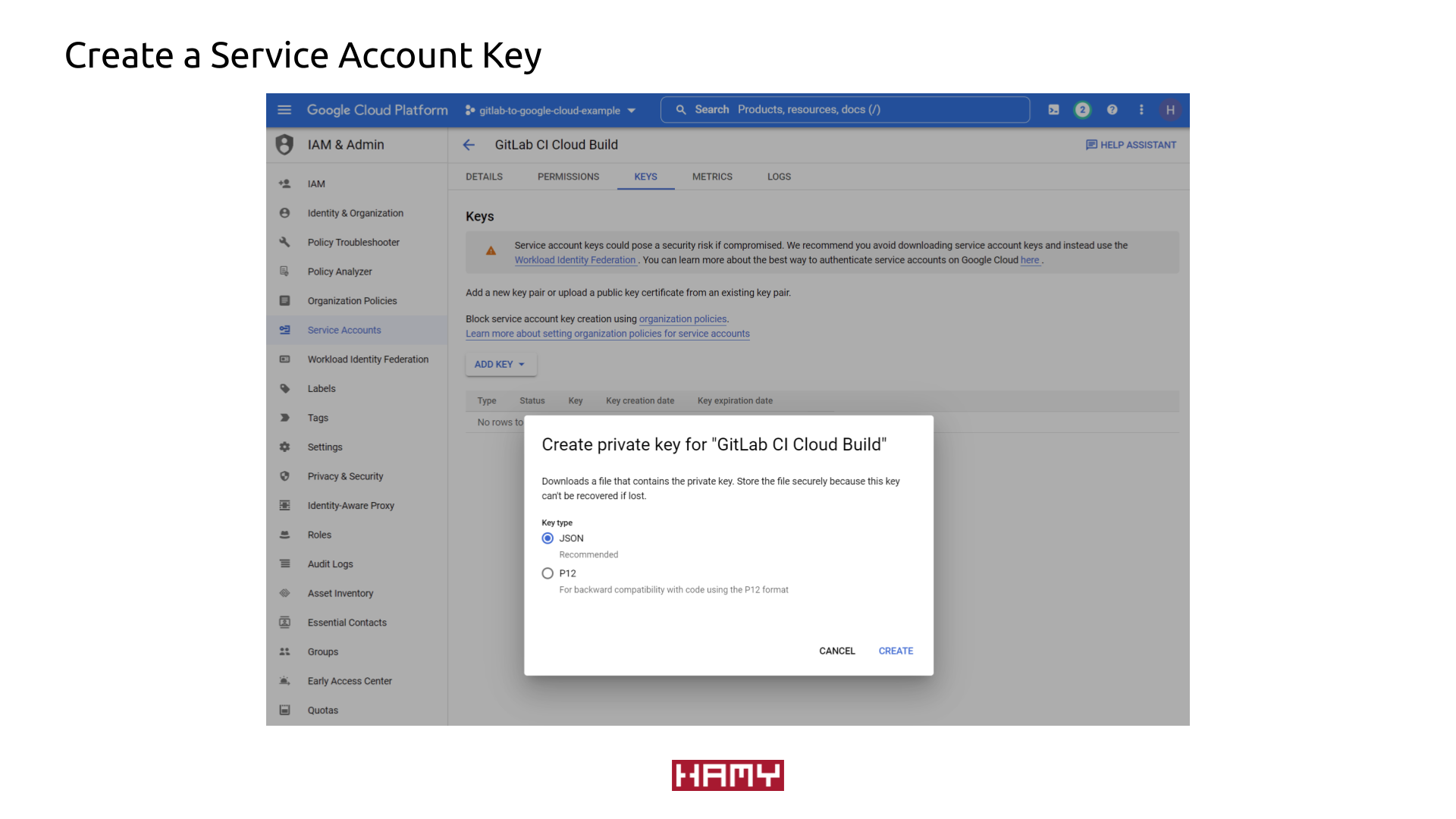
- Get access key to the Cloud Build Service account
- Go to the list of Service Accounts
- Click the new Service Account you created
- Click
Keystab Add Key > Create Key > JSON- Hold on to this key - we'll need it later! Will call it
GitLab CI Cloud Build Key
GitLab to Cloud Run
Now that we've got our Google Cloud project setup and ready to receive builds, we can setup our GitLab repo to trigger it.
CI Variables
The first thing we'll setup is our CI variables. These variables will be available to our CI jobs so that they can interact with Google Cloud successfully.
The two variables we need are:
- GCP_PROJECT_ID - The ID of your Google Cloud Project
- GCP_CLOUD_BUILD_SERVICE_KEY -
GitLab CI Cloud Build Key(the JSON file we created earlier)
We can set these variables by:
- Go to your GitLab repo
- Go to
Settings > CI/CD > Variables, clickExpand - Foreach variable
Add variable- Key -> the key from above
- Value -> the value
- Type -> Variable (yes, even for the JSON key - copy and paste it)
GitLab CI
Next we'll set up .gitlab-ci.yml. This is a special yaml config in the root of our repo that GitLab reads to determine what jobs it should run when we push.
.gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- deploy
deploy_prod:
stage: deploy
image: google/cloud-sdk:alpine
environment: PROD
only:
- master
script:
- echo $GCP_CLOUD_BUILD_SERVICE_KEY > /tmp/gcloud-service-key.json
- gcloud auth activate-service-account --key-file /tmp/gcloud-service-key.json
- gcloud config set project $GCP_PROJECT_ID
- gcloud builds submit . --config=cloudbuild.yaml
after_script:
- rm /tmp/gcloud-service-key.json
This file says:
- There's a deploy stage
- deploy_prod is part of the deploy stage and only runs on
masterbranch updates- Pull the Google Cloud SDK image
- Create a temporary json file from GCP_CLOUD_BUILD_SERVICE_KEY
- Authenticate with Google Cloud SDK with the service key
- Set the correct project from GCP_PROJECT_ID
- Trigger Cloud Build using
cloudbuild.yaml(which we'll make in a sec)
Cloud Build config
The final thing we need to do is setup our Cloud Build config. This tells Cloud Build what we want it to do when we trigger it from GitLab.
cloudbuild.yaml
steps:
# App
# [App] build the container image
- name: 'gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker'
args: [ 'build', '-t', 'gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/app', './App' ]
# [App] push the container image
- name: 'gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker'
args: [ 'push', 'gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/app']
# [App] deploy container to Cloud Run
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud"
args: [
'run',
'deploy',
'app',
'--image',
'gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/app',
'--region', 'us-central1',
'--platform', 'managed',
'--allow-unauthenticated']
# Web
# [Web] build the container image
- name: 'gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker'
args: [ 'build', '-t', 'gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/web', './Web' ]
# [Web] push the container image
- name: 'gcr.io/cloud-builders/docker'
args: [ 'push', 'gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/web']
# [Web] deploy the container to Cloud Run
- name: "gcr.io/cloud-builders/gcloud"
args: [
'run',
'deploy',
'web',
'--image',
'gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/web',
'--region', 'us-central1',
'--platform', 'managed',
'--allow-unauthenticated']
This file says:
- For each App and Web (these are the apps that come with CloudSeed):
- Build the container image using the Dockerfile in the appropriate folder
- Push the image to a specific folder
- Deploy the respective image to Cloud Run
Verify the deploy
To verify the deploy, we can:
- Check GitLab - see status of deployment pipeline at
CI/CD > Pipelines - Check Cloud Build - Check status of builds at
Cloud Build > History - Check Cloud Run - Check status of deploys at
Cloud Run > YOUR_SERVICE > Revisions
If there are any failures, you can find more information for debugging in the logs.
Further Reading
Want more like this?
The best way to support my work is to like / comment / share this post on your favorite socials.
